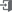While surfing the web, you may have seen that 'http' and 'https' are added to the homepage address bar first.
Do you know the difference between 'http' and 'https'?
Sometimes some websites have warnings such as 'The connection is not set to private',
'The secure connection (HTTPS) is not used' or 'Unsafe' when accessed.
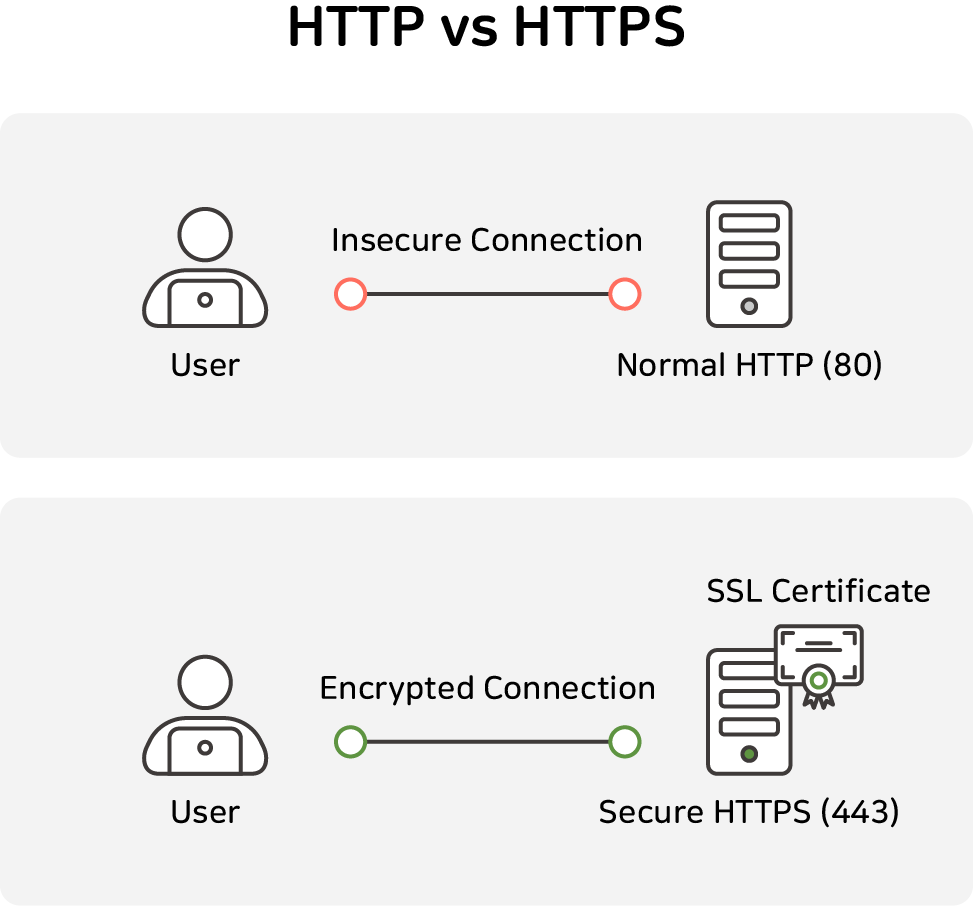
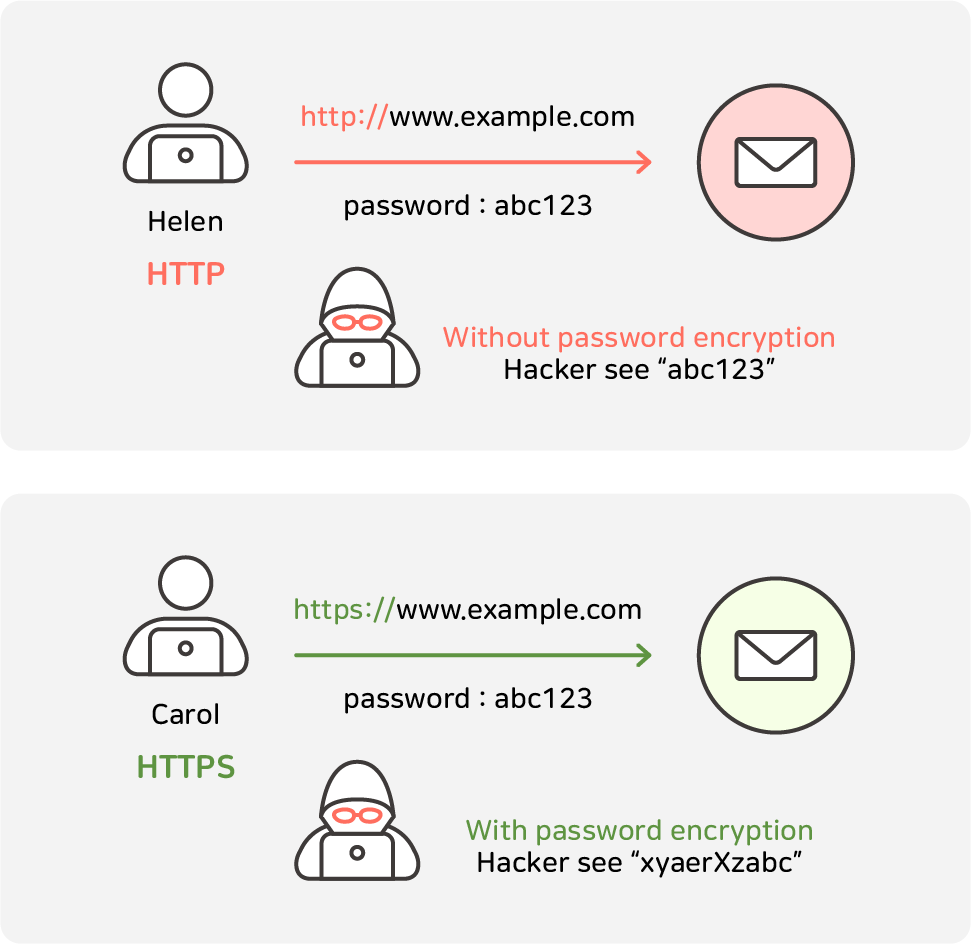
From this, we can see that HTTPS is a secure connection rather than an HTTP connection.
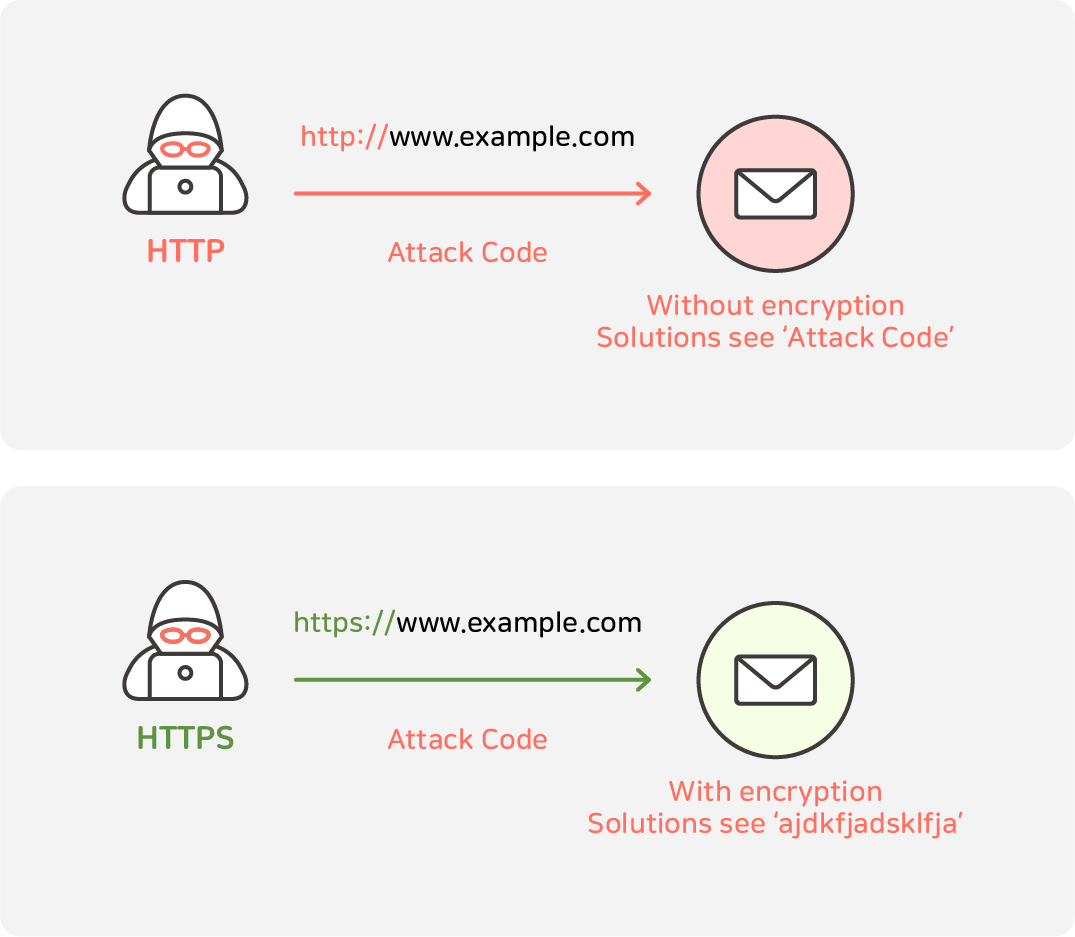
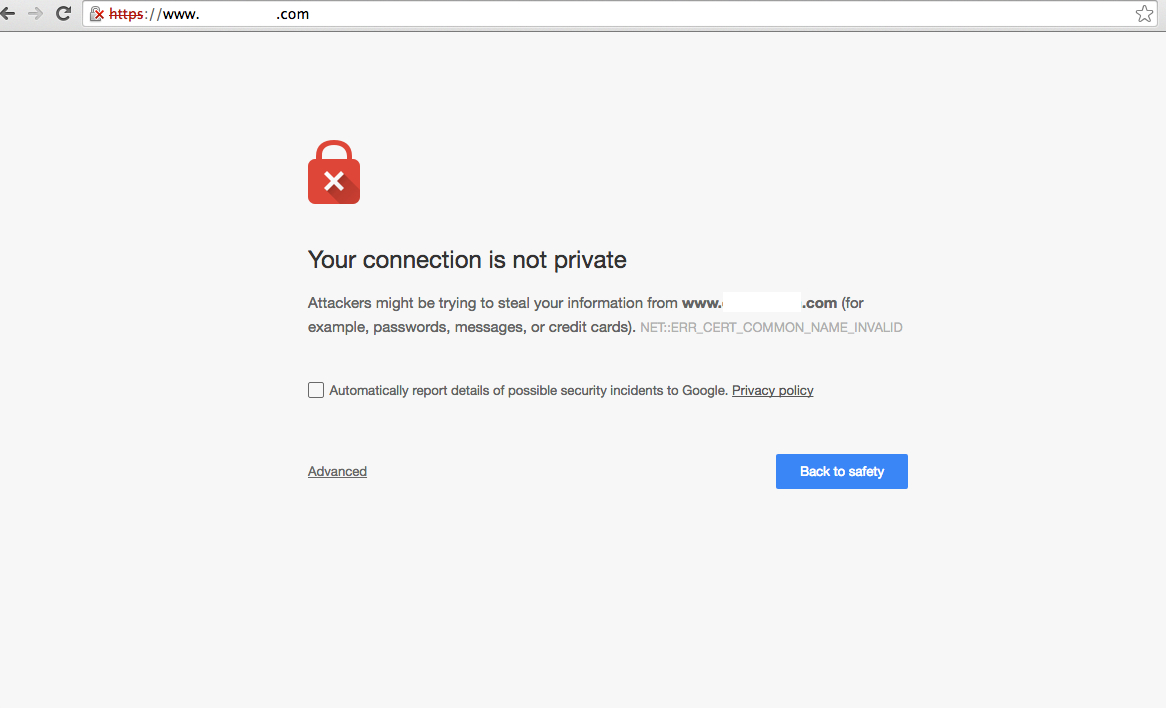
HTTP is a protocol that sends data in plaintext without encryption when users and servers exchange data.
Therefore, anyone can intercept and read data in the middle of communication.
HTTPS, on the other hand, uses the 'SSL/TLS' protocol to encrypt and securely send all the data it sends and receives.
Clients and servers use public/private key-based public-key encryption to encrypt and decrypt data.
HTTPS uses the 'SSL/TLS' protocol,
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) was developed in 1993 for secure communication between web servers and browsers,
and three versions have been released from 1.0 to 3.0.
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is an upgraded protocol based on SSL 3.0
and has now been released up to TLS 1.3.

Encrypted traffic using SSL/TLS includes HTTPS,
as well as encrypted mail transfer protocols SMTPS, POP3S,
and encrypted file transfer protocols FTPS.
If an intermediary attempts to read encrypted traffic by intercepting the data,
only encrypted data can be verified, and the data cannot be read because
there is no shared secret key between the 'client' and the 'server'.
This more secure encrypted transmission method was first used by services
dealing with sensitive data such as personal information,
and now more than 90% of websites support HTTPS.
With the increasing transmission of encrypted traffic,
web attackers have begun to attack through encrypted traffic rather than plaintext,
and about 80% of advanced persistent threat (APT) attacks are now through encrypted traffic.
Attacks through encrypted traffic mean that security products should check all encrypted traffic, not just plaintext data.
The 'decryption' operation, in which a security product located between 'client' and 'server' decrypts encrypted traffic,
re-encrypts, and sends a request to the 'server', which requires significant resources.
This can lead to performance degradation of the security solution,
and traditional security solutions send encrypted traffic immediately without checking the data, leading to a breach.
Only about 20% of security equipment is known to be capable of complete encryption,
and some encrypted traffic should not be decrypted, such as "financial information used in Internet banking",
so it is also necessary to distinguish them.
To solve these issues, SSL visibility appliance has emerged to act as a "decryption" for encrypted traffic.
MONITORAPP's AISVA is an SSL visibility appliance,
a solution dedicated to SSL/TLS traffic encryption that provides visibility to security solutions
such as network security systems, IDS, and log collection servers.
The data flow through AISVA is as follows.

- 1. AISVA decrypts the encrypted traffic first.
- 2. Send decrypted plaintext traffic to a firewall or other security system sections such as IPS, DLP, and APT.
- 3. Plain text traffic that has passed the security policy is again received by AISVA.
- 4. AISVA will re-encrypt and send it to the server.
Through these procedures, security products can reduce the burden of traffic decryption and prevent possible violations.
In addition to simply encrypting SSL/TLS traffic, AISVA offers several features.

'Security system interworking section health check'
that automatically performs traffic bypass and ensures service availability
if there is a problem between AISVA and the security system interworking section.
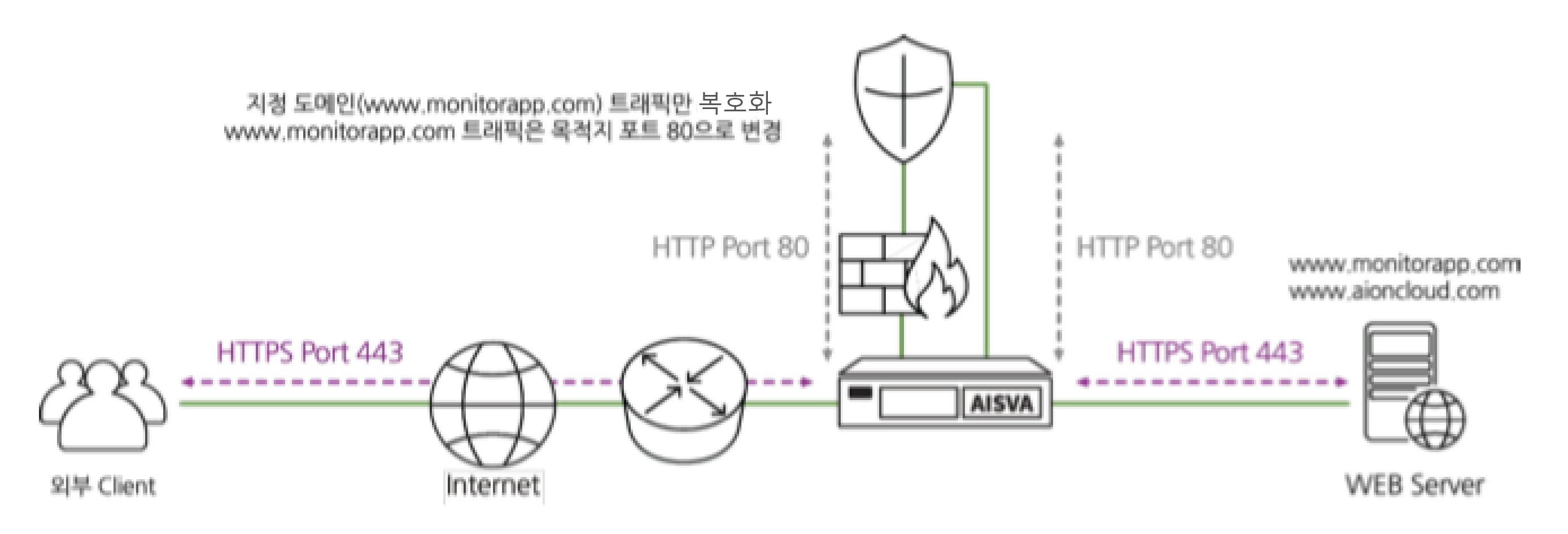
'Selective decryption for specified domains' allows you to perform decryption only for specific domains
when multiple web services are provided on the same server.
'Invalid SSL certificate detection', which blocks sessions if an invalid certificate is used.

In addition, it provides PKP (Public Key Pinning), 'certificate distribution and status management',
'monitoring of the system, traffic, and decryption status',

and can handle inbound and outbound bi-directional traffic, making it a complete SSL visibility appliance.
AISVA supports a variety of network configurations.

It supports an environment where security equipment that changes session information such as NAT (Network Address Translation)
can be configured and interconnected in the active inline section, and it also supports asynchronous traffic environments.
AISVA can be configured as a 'full transparent mode of the proxy base' and can be operated in 'stealth mode' without granting a separate IP,
so there is no change or impact on the existing network configuration environment.
The emergence of SSL/TLS has brought us a secure web environment with encrypted data communication.
However, attackers also use the same encrypted traffic, and security equipment struggles to decrypt SSL/TLS traffic for a variety of reasons.
SSL visibility appliance that specialize in decrypting SSL/TLS traffic are a necessity, not an option.
Protect your organization's assets more securely with AISVA, which provides complete SSL visibility and add-ons.