Weekly web attack trends
You can analyze weekly web attack trends to see when web attacks are concentrated at any given time. Based on this, you can use it to plan proactive prevention and response strategies for high attack periods.
The graph below visualizes the number of web attacks detected by AIWAF during the month of March 2025, on a weekly basis.
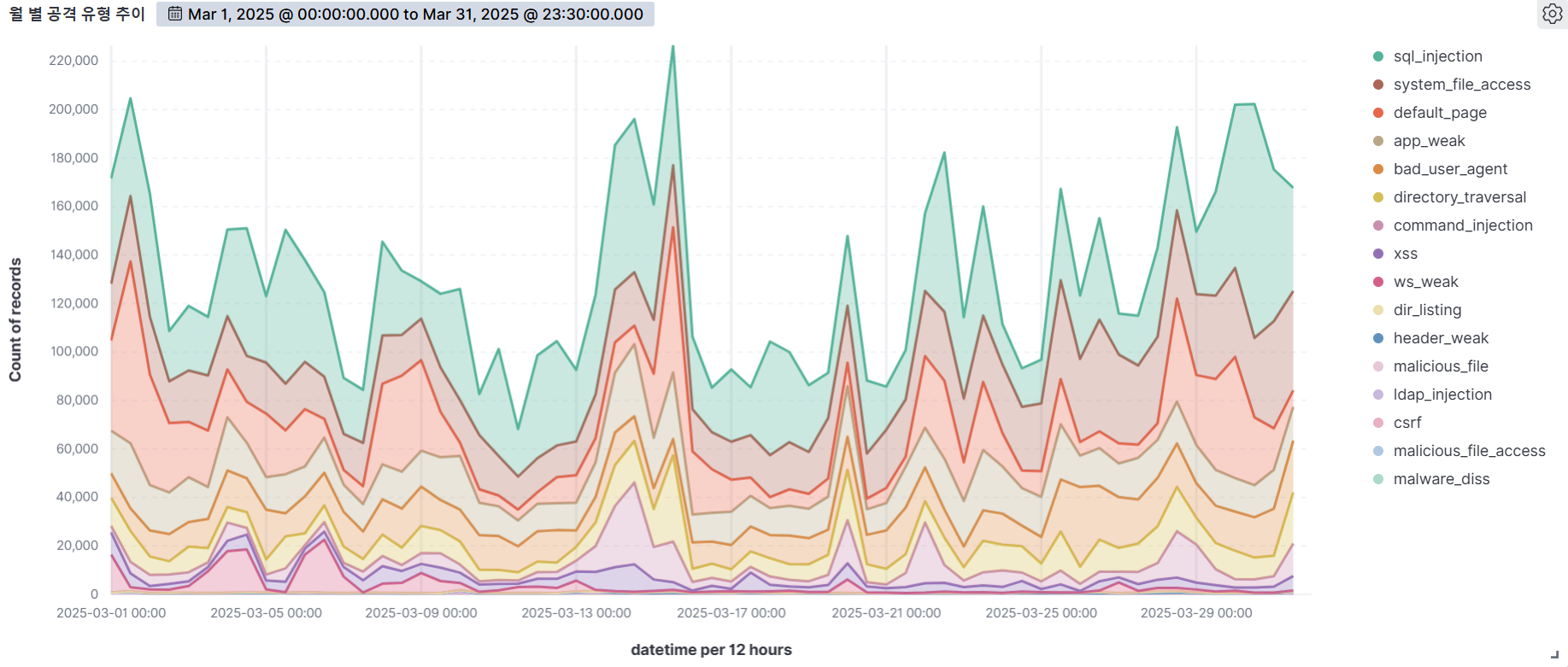
Analyzing AIWAF detected data for the month of March 2025, we detected an average of approximately 260,000+ web attacks per day, an increase from the previous month, indicating that the threats to web servers are continuing to become more sophisticated. We also observed a higher frequency of attacks on weekends (Saturday and Sunday) than on weekdays, which may indicate a strategic approach to take advantage of lower web server utilization during non-business hours.
Notably, March 15 was the most intensive day for web attacks during the entire period, with SQL Injection accounting for the highest percentage of attack types detected on that day. SQL Injection is a common attack method that manipulates databases to take over system privileges or steal internal information. Attackers often use this technique to bypass a system's user authentication process or to gain insight into the database structure, which makes it especially important for organizations to protect their sensitive information. In fact, AIWAF categorizes SQL Injection as a high-risk attack type with the most detection patterns. The results of this analysis show that major web attack types, including SQL Injection, require continued attention and sophisticated countermeasure strategies, and will provide an important basis for future detection and blocking policies.
Web attack trends by attack type
By analyzing web attack trends by attack type based on detection logs, you can systematically identify which types of attacks are most frequent over the course of a month. This analysis is more than just a statistic; it is a key reference point for refining your organization's security policy and response.
Analyzing the detection logs collected by AIWAF during the month of March 2025, we detected a wide range of web attacks, some of which showed distinct patterns, such as being concentrated in certain time periods or accounting for a high percentage of the total number of attacks. In particular, classic and still threatening attack types, such as SQL Injection and System File Access, are at the top of the list, and they tend to be carried out repeatedly, often by automated attack tools or botnets.
The graph below visualizes the distribution of web attack types detected by AIWAF as of March 2025.
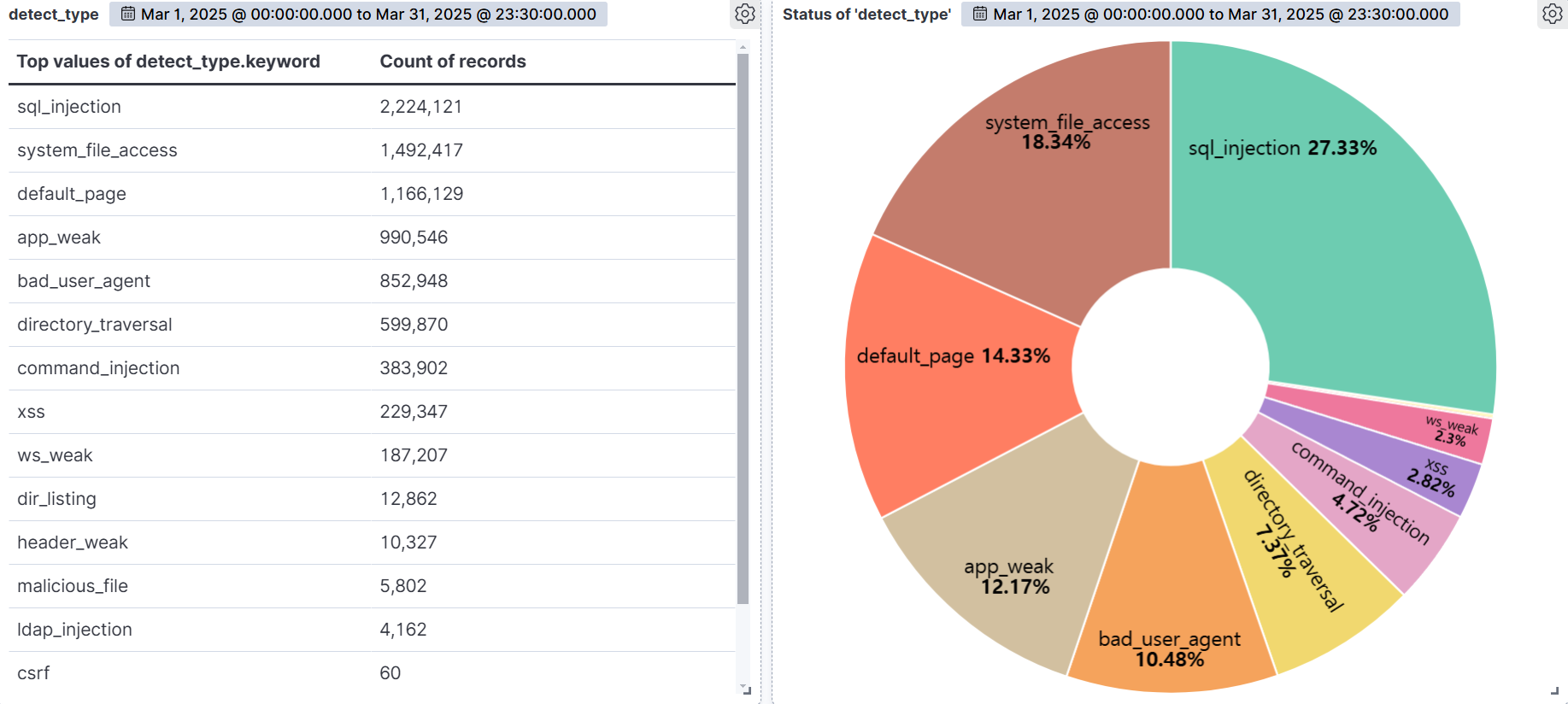
According to the statistics by type of web attack detected by AIWAF in the month of March 2025, SQL Injection was the most prevalent, accounting for 27.33% of all detections. This was followed by System File Access (18.34%), Default Page (14.33%), and App Weak (12.17%). This suggests the need for more precise responses and proactive measures against this particular type of attack.
First of all, SQL Injection is a type of attack that is always high on the OWASP Top 10, and the attack techniques are highly evolving. This attack typically occurs when values passed via user input are embedded in SQL queries and executed verbatim, which can be exploited by an attacker to bypass improper authentication, view database structures, steal sensitive data, and more. Applications are particularly vulnerable to this attack if they use dynamic queries or lack validation of input values.
System File Access (18.34%), the second highest percentage, refers to attempts by attackers to exploit vulnerabilities in web applications to gain unauthorized access to files and directories inside the system or to manipulate arbitrary files. These attacks can be caused by web server configuration issues, insufficient access controls, directory path validation failures, etc. and can lead to system privilege takeover or backdoor installation if successful.
The third highest category, Default Page (14.33%), targets pages that retain their initial settings after installation or system message pages. They expose information during the information gathering phase that can be used in subsequent attacks to determine the type of software and configuration of the system. While this attack type is largely passive, it is often detected in high volume by automated scanners, making early detection and response critical.
App Weakness (12.17%), the fourth most common attack type, targets security flaws in the application itself, such as lack of authentication, session management vulnerabilities, and misconfigurations. It has been increasingly detected in cloud-based SaaS systems and API-based services in the form of authentication bypass attempts and API abuse, which may have implications for future cloud security policy formulation.
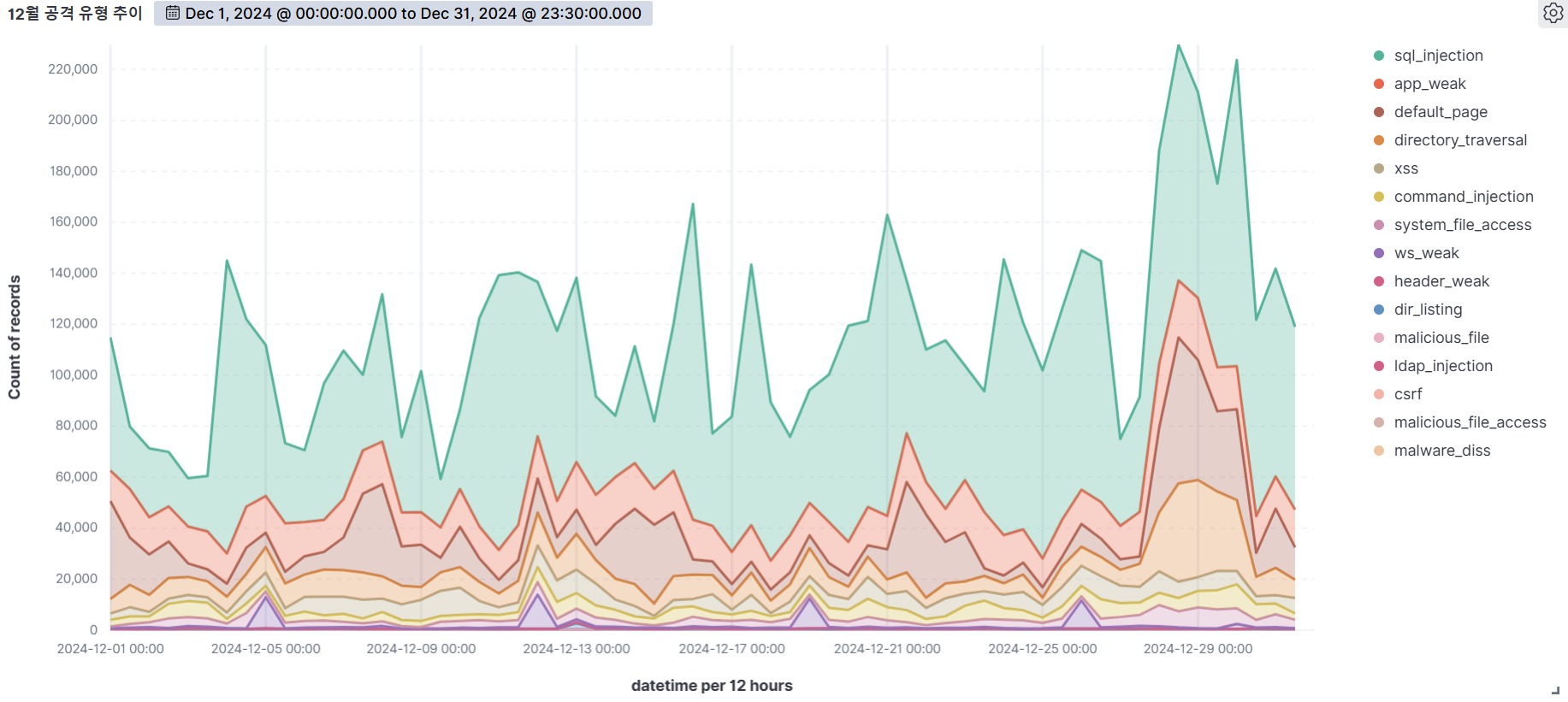
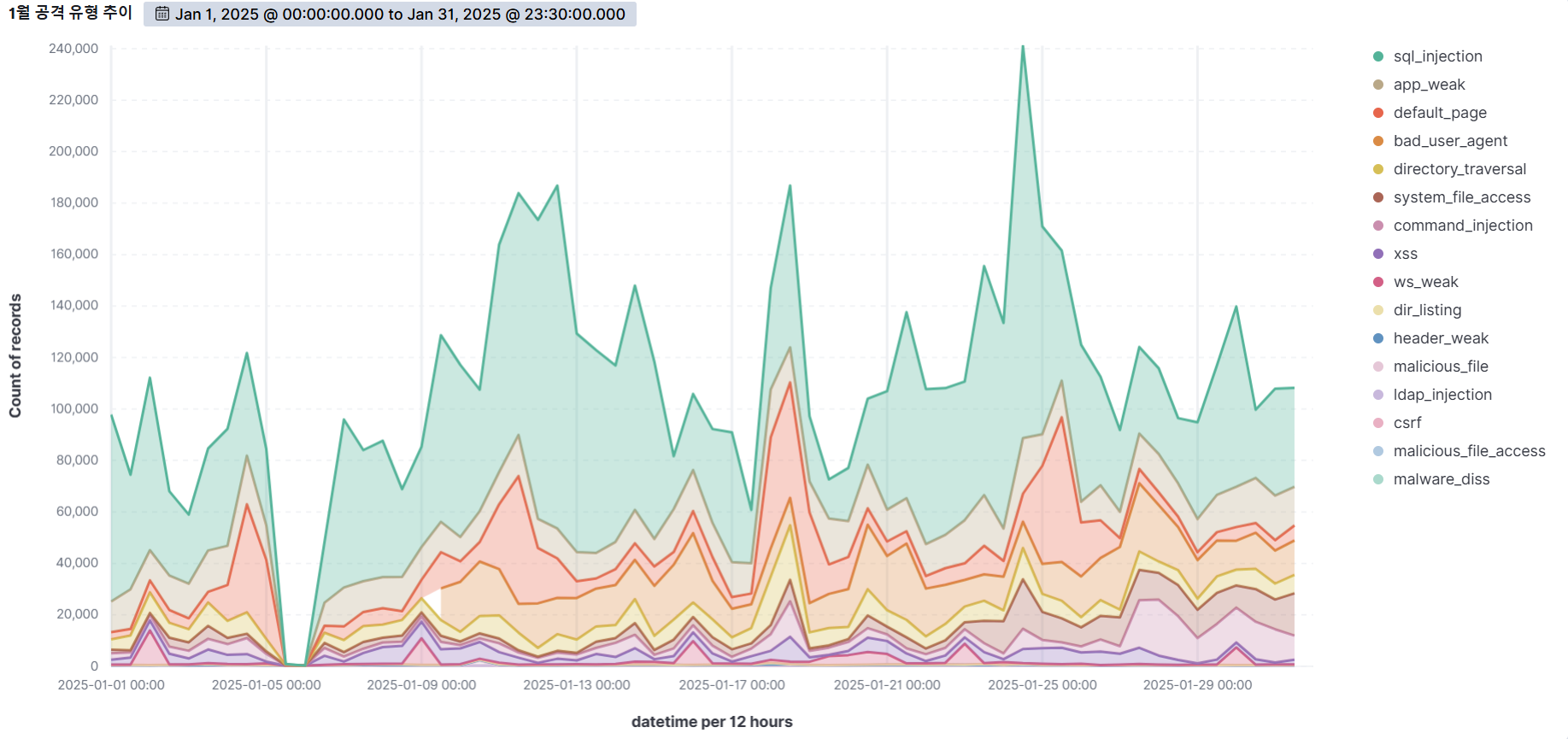
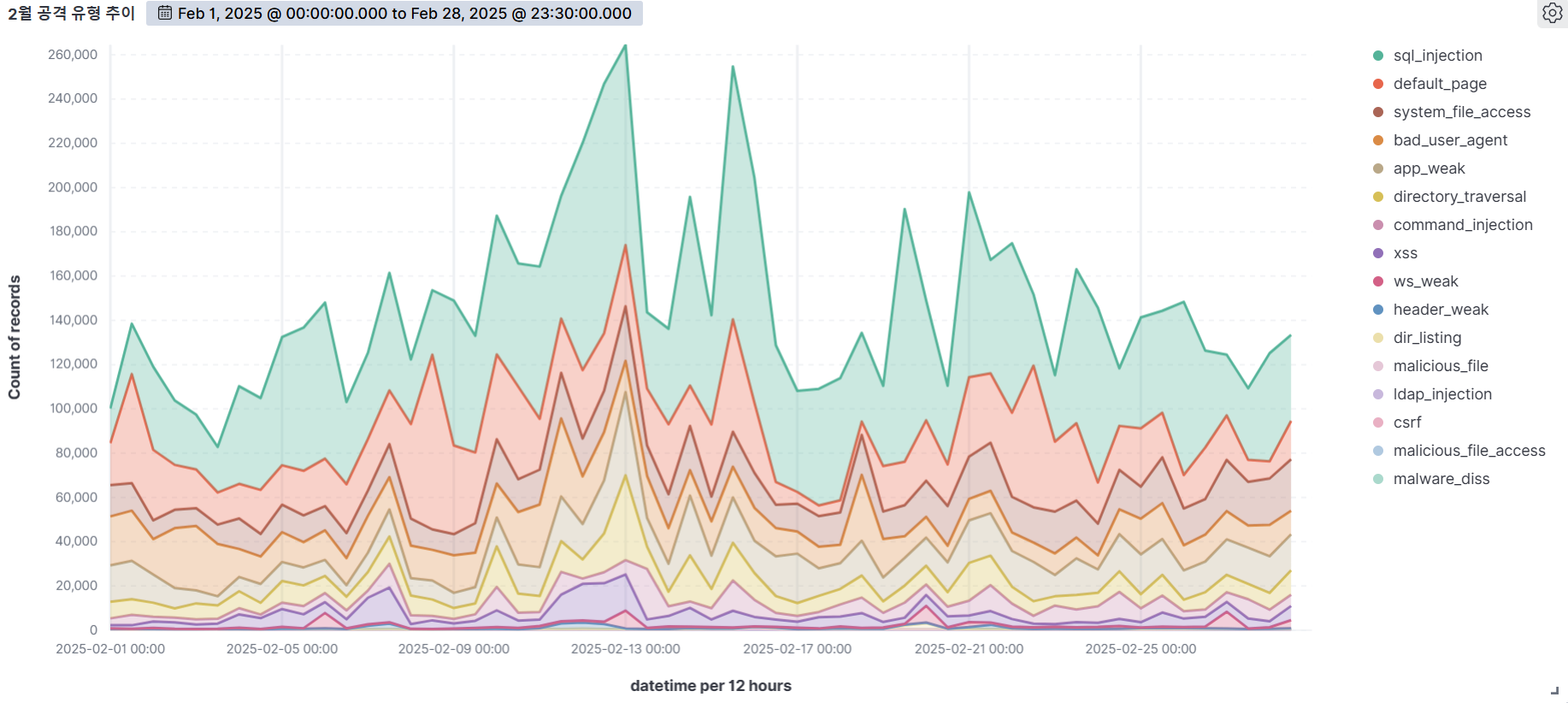
Summary of web attack trend graphs for the last 3 months
December
January
February
Top 30 Attacker IPs

Vulnerability analysis reports
Ivanti vTM Authentication Bypass
1. Overview
Ivanti Virtual Traffic Manager (vTM) is a software-based application delivery controller (ADC) that is responsible for efficiently managing and optimizing application traffic on a network. The platform is primarily used to improve the performance and security of web applications and has the advantage of being flexible enough to be deployed in a variety of environments.
Last year, a serious security vulnerability was discovered in Ivanti vTM, CVE-2024-7593, which allows authentication bypass. This article provides an overview of the vulnerability, a comprehensive analysis of how it works, what environments may be affected, and security mitigations.

Source : https://thehackernews.com/2024/10/ivanti-endpoint-manager-flaw-actively.html
2. Attack types
CVE-2024-7593 is a critical authentication bypass vulnerability found in Ivanti vTM that exploits a design flaw in the internal authentication algorithm to allow an attacker to gain unauthorized access to any section of the web interface. This vulnerability is particularly dangerous because it allows an attacker to arbitrarily create an account with administrator privileges by bypassing access controls on an endpoint called wizard.cgi.
To gain access to the wizard.cgi endpoint, an attacker would first set the value of error, one of the parameters in the request, to 1. This simple manipulation is enough to defeat existing access control logic, resulting in access to the admin settings page without authentication.
The attacker then leverages the section parameter to load a specific configuration section related to account creation. As a next step, by injecting manipulated data into the request's body, the attacker can bypass Ivanti vTM's Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) prevention policy, and finally succeed in adding a new administrator privileged account to the system.
This vulnerability is a prime example of poorly implemented authentication and session management functionality, and is a dangerous vulnerability that could compromise the overall security of your system. Organizations using Ivanti vTM should immediately check to see if they have applied a security patch for this vulnerability and take appropriate security measures as soon as possible.
The attack request to bypass access controls and create an administrator account contains specific parameters, which are used to bypass Ivanti vTM's CSRF prevention mechanisms and lead to account creation.
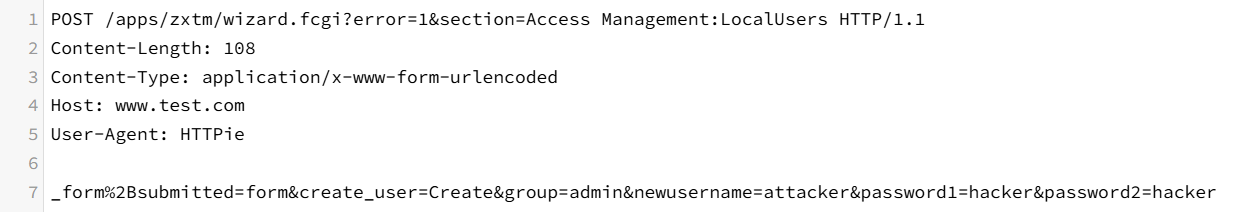
- _form_submitted=form: Flag for bypassing CSRF protection
- create_user=Create: Show request to create admin account
An attacker can bypass the authentication process and create a new administrator account on the system by accessing the wizard.cgi endpoint as described above and sending an HTTP request with the parameter values above.
3. What to do
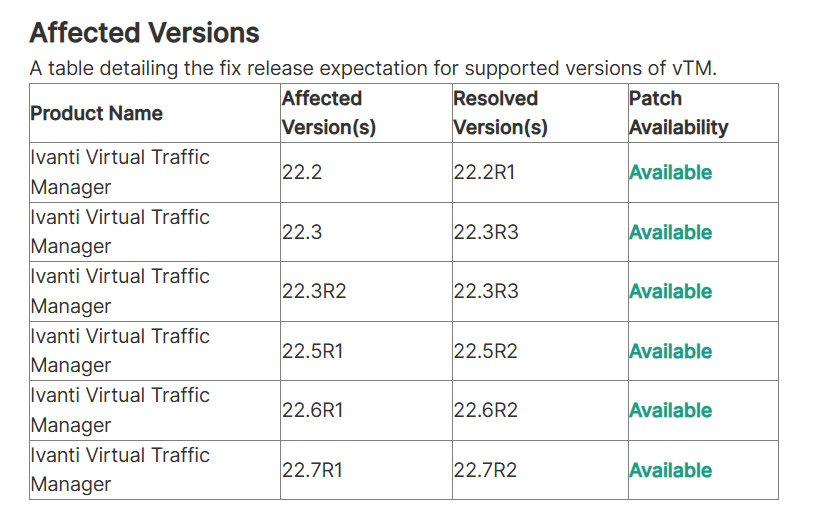
Ivanti has recognized the severity of the CVE-2024-7593 vulnerability and has officially released a security patch for it. Due to the dangerous nature of the vulnerability, which could allow an attacker to gain administrator privileges through authentication bypass, Ivanti has advised product users to update as soon as possible. To this end, Ivanti has specified a minimum patch version for each product version that resolves the vulnerability, and organizations running Ivanti vTM must update to that version or higher, as shown in the image below.
If security patches are not applied, an attacker could potentially create an administrator account without authentication and take full control of the system, so prompt security updates are of utmost importance.
To further strengthen our response to this vulnerability, our AIWAF products have also added pattern signatures to detect and block this attack with the February 2025 pattern update. Specifically, we added Pattern ID 2235: Ivanti vTM Authentication Bypass, which is designed to detect suspicious requests in real-time and proactively block attempts to create administrator accounts.
For Ivanti vTM users, a multi-layered defense with a security solution like AIWAF alongside security patching of the product itself can be a very effective mitigation strategy.
Source : https://forums.ivanti.com/s/article/Security-Advisory-Ivanti-Virtual-Traffic-Manager-vTM-CVE-2024-7593
4. Conclusion
Ivanti vTM is primarily utilized by large enterprises and organizations with complex networks and IT infrastructures. As such, Ivanti vTM plays a key role in service availability, security, and scalability, and has a significant system-wide impact.
The CVE-2024-7593 authentication bypass vulnerability is a serious flaw that could fundamentally threaten the security architecture of Ivanti vTM, with a very high score of 9.8 on the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), meaning that it could lead to near-complete privilege escalation, a dangerous level that could allow an attacker to bypass authentication procedures and gain administrative privileges.
As a result, the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Administration (CISA) quickly placed the vulnerability on its urgent patch target list, Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV), which indicates that it has been determined to have a very high potential for real-world exploitation, and is a critical issue that requires a quick response from affected system administrators.
It is therefore important for organizations running Ivanti vTM to immediately apply security patches for this vulnerability, and to proactively respond to potential security threats by building a defense in conjunction with security solutions such as WAFs.
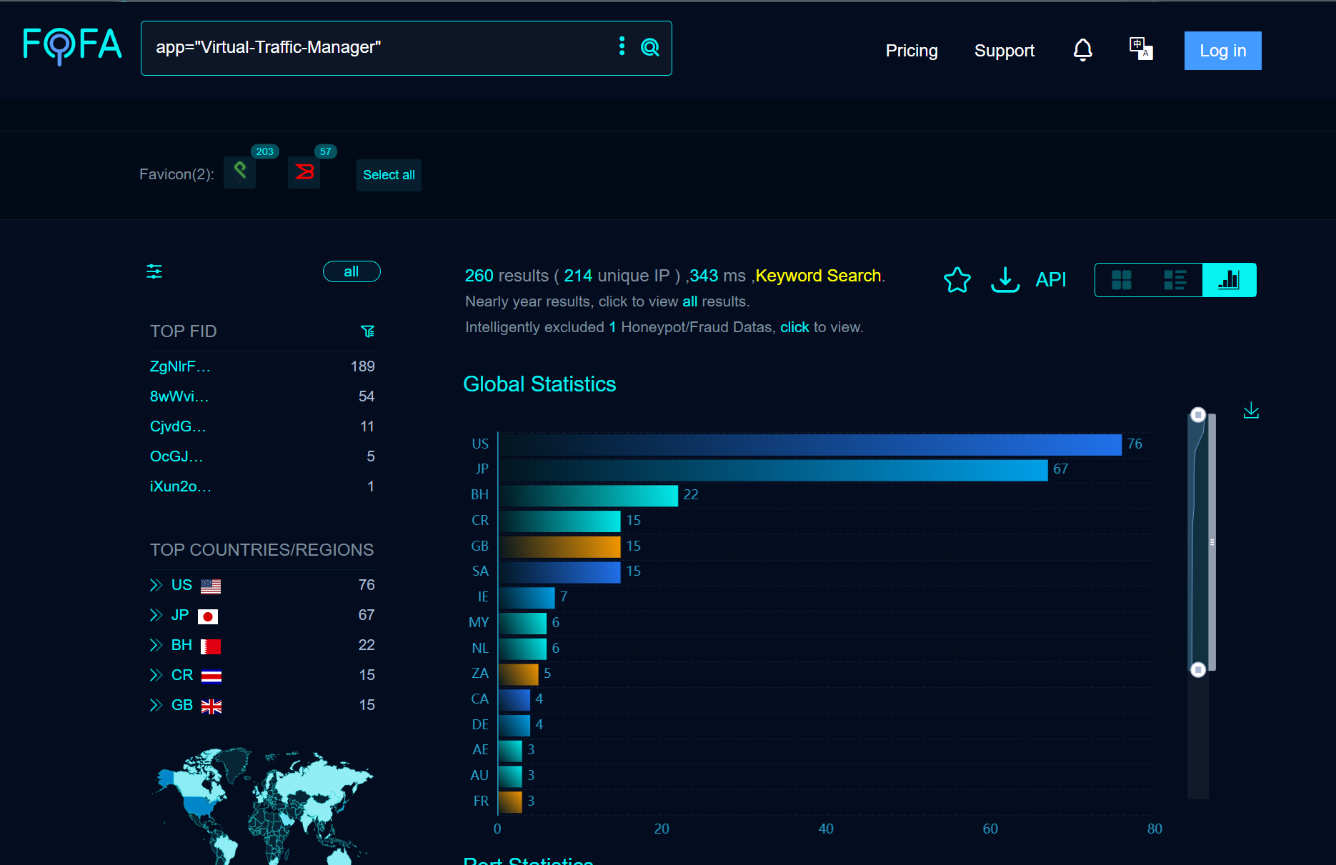
Source : https://en.fofa.info/result?qbase64=YXBwPSJWaXJ0dWFsLVRyYWZmaWMtTWFuYWdlciI%3D
Our AIWAF product is continuously developing and adapting proprietary detection patterns to respond quickly and effectively to a wide range of security vulnerabilities in the Ivanti family.
AIWAF develops pattern signatures that match the nature of the threat and the attack method to provide real-time detection and blocking for both previously reported vulnerabilities and newly discovered vulnerabilities. With this approach, AIWAF goes beyond simple pattern matching to perform behavior-based analysis of attacks, enabling a more intelligent and proactive security response.
We will continue to provide rapid and continuous response to security threats against the Ivanti family of products, and we are committed to helping our customers keep their assets safe through regular pattern updates that reflect the latest security trends and threat intelligence.
5. References
- https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/cve-2024-7593
- https://socradar.io/critical-ivanti-vtm-vulnerability-exploited-cve-2024-7593-pgadmin-flaw-could-expose-data-cve-2024-9014/
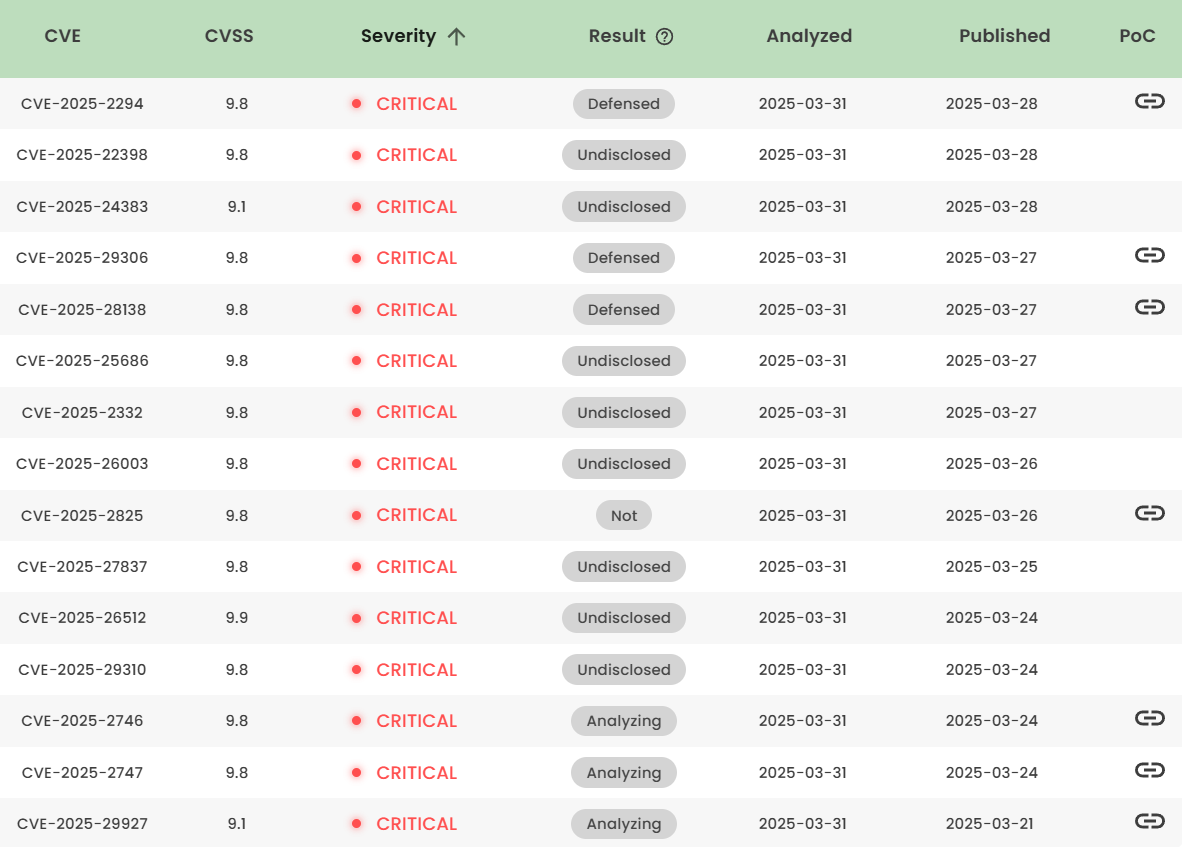
Latest vulnerability CVE status
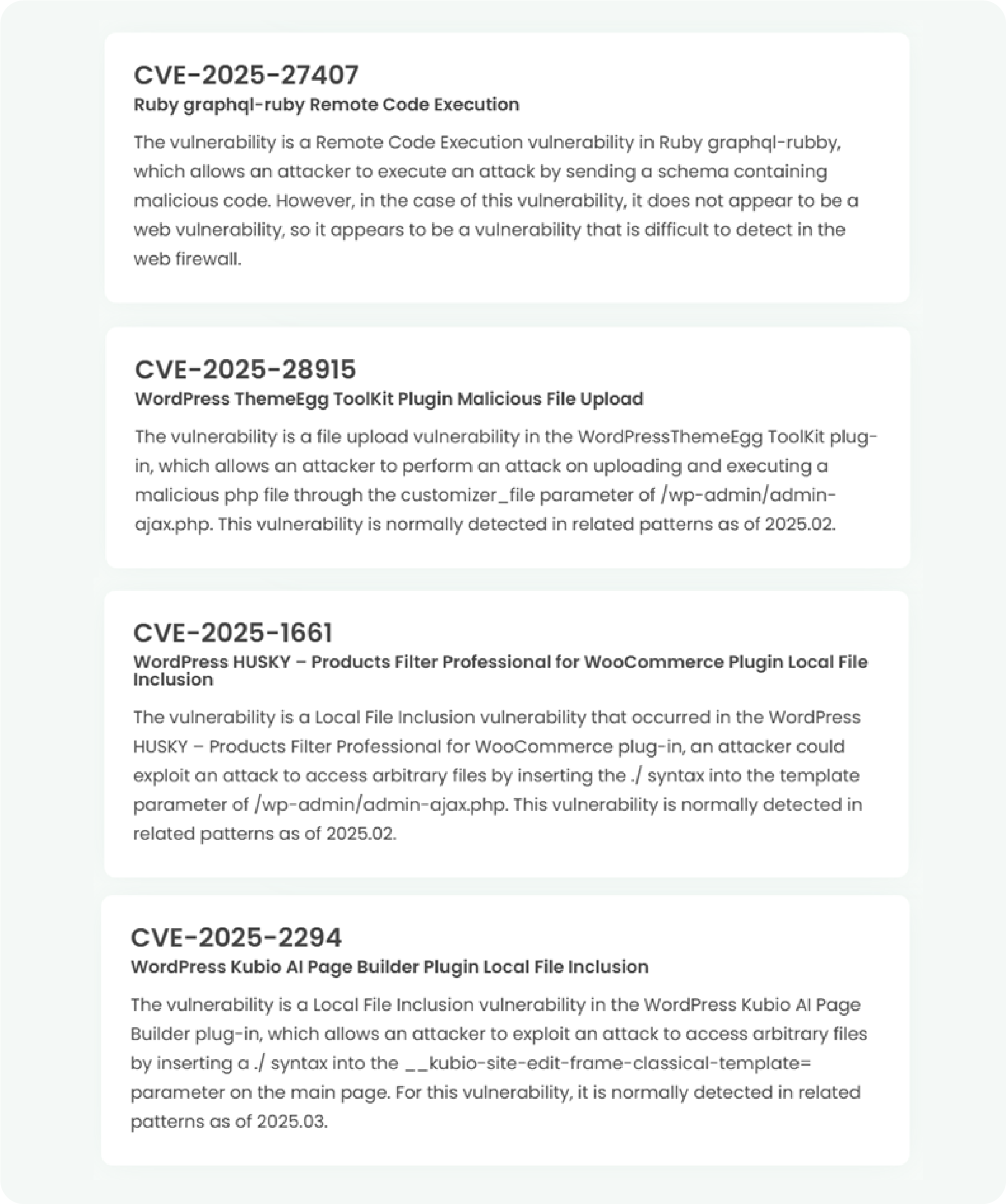
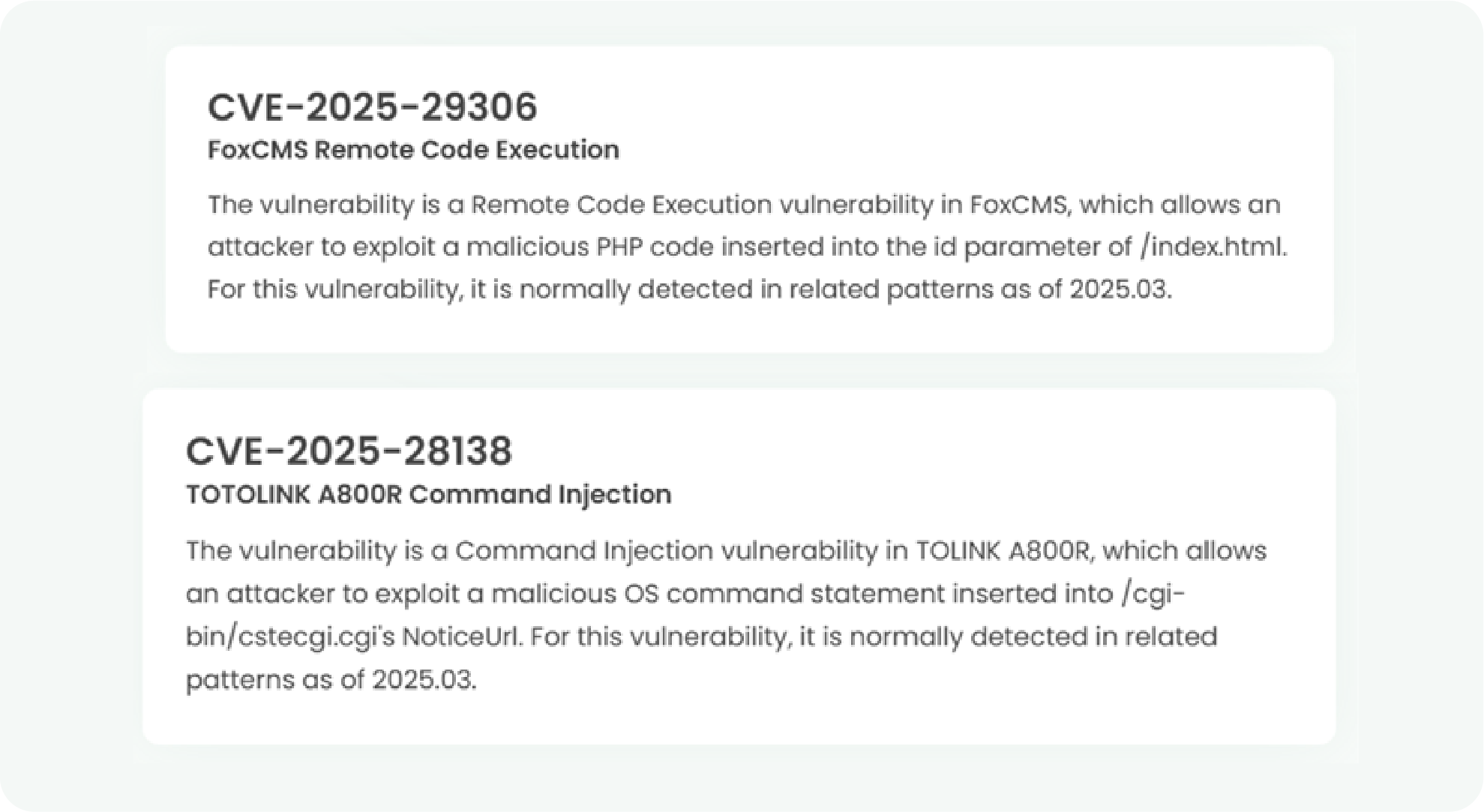
1. High-risk vulnerability status (2025.03)
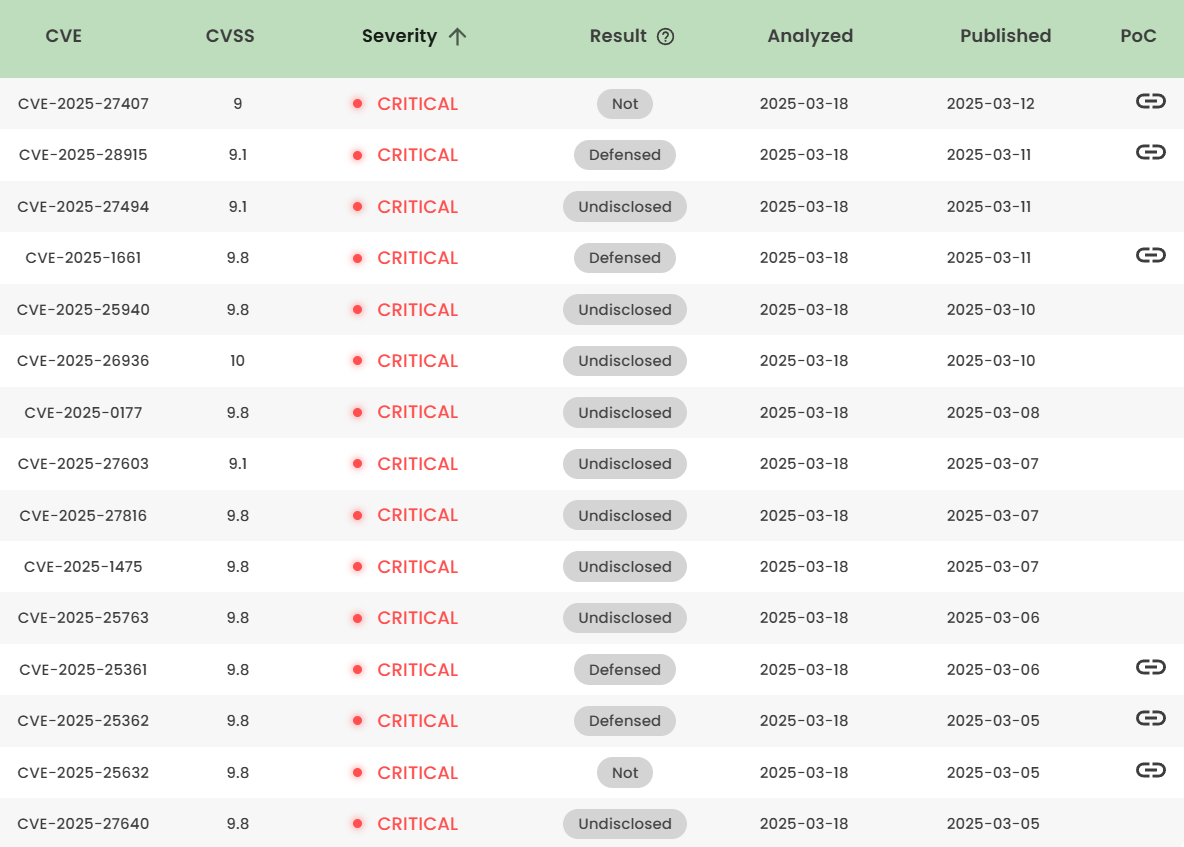
2. High-risk vulnerability descriptions